
Influence of sex hormones on cancer progression. Cancer screening in the United States, 2017: a review of current American cancer society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. Global, regional, and national age–sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012 v1.0. Further studies exploring the link between intrauterine hormone environment and cancer risk are encouraged.
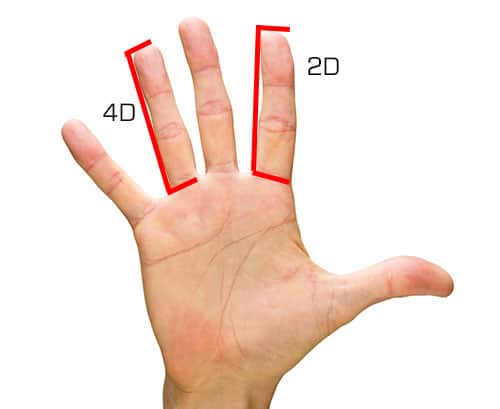
Sex hormone environment during early development is associated with cancer risk later in life. The meta-analyses demonstrated that testicular cancer was not associated with right-hand 2D : 4D ratio ( p = 0.74) and gastric cancer was not associated with right-hand ( p = 0.15) and left-hand ( p = 0.95) 2D : 4D ratio. Greater 2D : 4D ratio was associated with younger presentation of breast cancer and brain tumors. The 2D : 4D ratio was not associated with prostate, breast, and gastric cancer stage. Low 2D : 4D was associated with prostate cancer, gastric cancer, and brain tumors, while high 2D : 4D, with breast cancer risk and cervical dysplasia. The 2D : 4D ratio was studied in prostate cancer, breast cancer, testicular cancer, gastric cancer, oral cancer, brain tumors, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Nineteen studies were included in the qualitative analysis. Studies that evaluated the association of 2D : 4D with cancer risk were collected from Pubmed/MEDLINE and Clarivate Analytics databases. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the association of 2D : 4D with cancer diagnosis, malignancy, and age at presentation. These results probably reflect the organizational benefits of prenatal testosterone.Intrauterine sex hormone environment as indicated by the second to the fourth digit ratio (2D : 4D) can be associated with cancer risk.

Female players with lower digit ratios tended to perform better in several aspects of basketball, especially defensively, and were more likely to be starters, suggesting they are the best players on the team in their positions. This study found evidence that 2D:4D was a correlate of performance in an open-skill sport. Mean 2D:4D differed by position in the starting lineup, as females with lower 2D:4Ds were more likely to be in the starting lineup. Unpaired t-tests were used to quantify differences in mean 2D:4Ds between starting and reserve players.ĢD:4D was a substantial negative correlate of blocks, rebounds, and field-goal percentage meaning, females with lower 2D:4Ds were generally better defensively as they recorded more blocks and rebounds, and were more efficient scorers, irrespective of their age and body size. Partial correlations (adjusted for age and body mass index) were used to quantify relationships between right and left 2D:4Ds and game-related statistics. Using a cross-sectional design, 64 female basketball players who competed in the South Australian Premier League were measured in-season for height, mass, and 2D:4D, with game-related statistics collected end-season. The secondary aim was to quantify the differences in mean 2D:4Ds between players based on their position in the starting lineup. High levels of prenatal testosterone and low levels of prenatal estrogens are associated with a low 2D:4D ratio, and men usually have a lower 2D:4D ratio than women (Manning, 2002). The primary aim was to quantify relationships between 2D:4D and game-related statistics in semi-professional female basketball players. The ratio of index finger to ring finger length (2D:4D) is an index of prenatal exposure to testosterone and estrogen (Lutchmaya et al., 2004, Manning, 2002). Digit ratio (2D:4D) is a negative correlate of sports performance, although this relationship may be weak in open-skill sports such as basketball.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
